A detailed insight on virus
A virus is a biological agent that reproduces inside the cells of living hosts. When infected by a virus, a host cell is forced to produce thousands of identical copies of the original virus an extraordinary rate.
There are various types of viruses in the world, As a representative of
viruses, T2 Phage is itroduced here with its importance.
Test your self with these biology questions
Structure of virus: T2 Phage is a cellular. Its body is divided into two parts- head and tail; the head is a hexagonal and the tail is rod shaped, a protein shell surrounds the body. Inside the shell there is a' double-strand DNA in its head. At the upper end of the tail there is a collar, and at the lower end there is a base plate, some spikes and attachment fibres. In Viruses there is no nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm and other organelles.
Multiplication of virus
Viruses can multiply only inside some other living cells. T2 Phage attacks a Bacterium. It keeps the protein shell outside; its DNA enters into the Bacterial cell. Later on it (the Viral DNA) makes the Bacterial DNA inactive and make many new Viruses. Ultimately the Bacterial cell is destroyed and new Viruses came out.
Importance:
(l) T2 Phage kills Bacteria, (2) Widely used m GeneticEngineering.
Importance of Viruses:
Deadly human diseases like Measles, Pox, Polio, Hydrophobia, Influenza,
Harpies, Viral hepatitis etc. are caused by Viruses. Viruses cause about 300 diseases of various plants and crops. Many diseases of domestic animals like - Cow, Goat, Pig, etc. are caused by Viruses. Vrtises are also responsible for fatal diseases like - AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome), Cancer etc.
Vaccines of several diseases like -Pox, Polio, and Hydrophobia etc. are also
produced 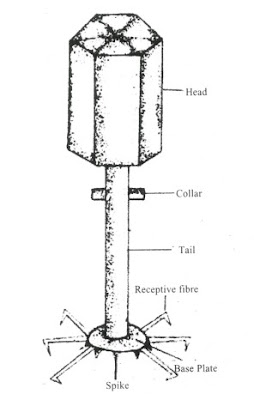






No comments:
Post a Comment